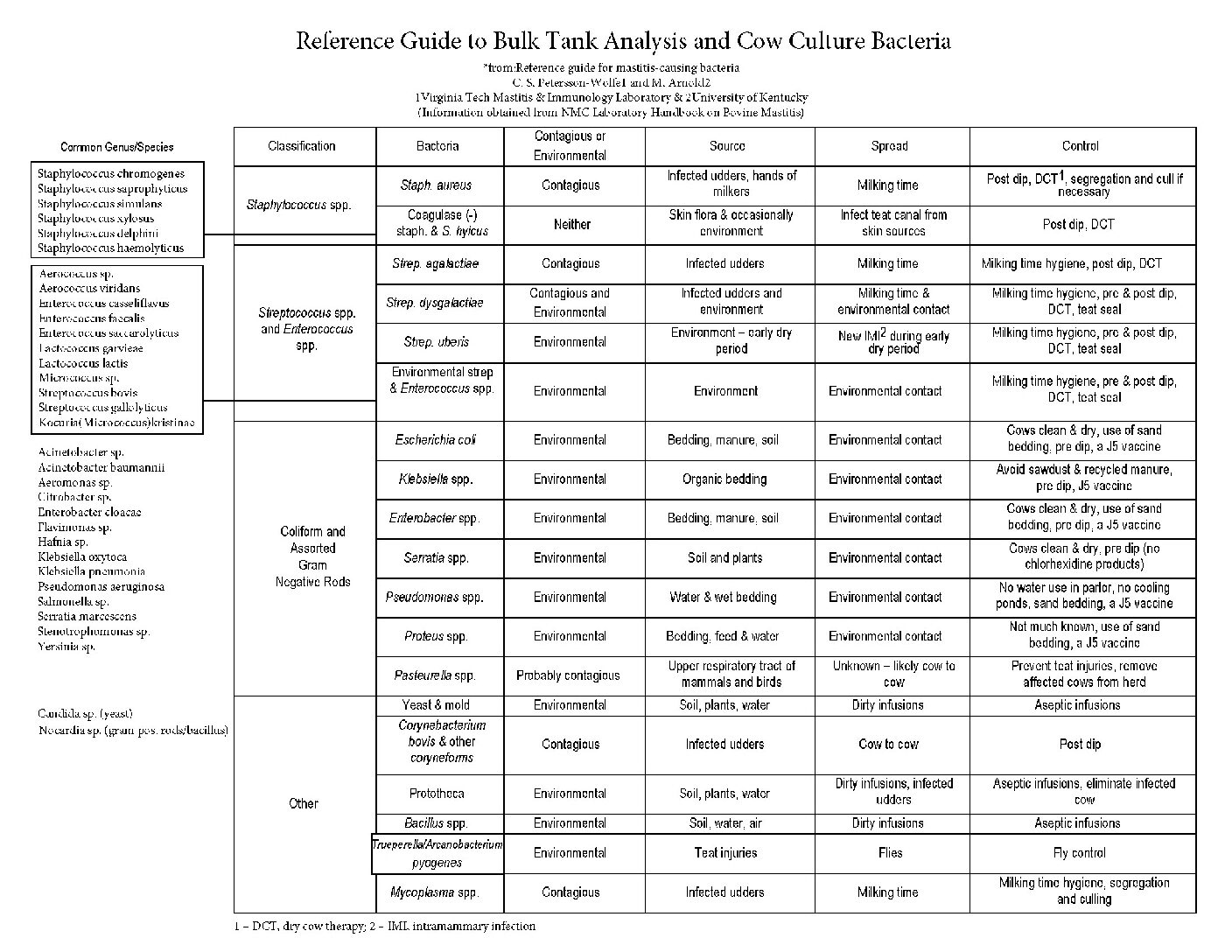
The microbiology of milk can be vital to management of dairy herds, especially milk quality. CLS utilizes Shimadzu Confidence MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, paired with the SARAMIS database, to identify bacteria and other microorganisms.
Articles and Resources
Cornell Dairy Science Info. Sheets
Directions on collecting clean milk samples for testing
Factsheet and Resources on Mastitis – University of Minnesota Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory
Mastitis in Cattle – Merck Veterinary Manual
Interpreting Lab Results (Minnesota DHIA)
NMC 10 Point Mastitis Control Program